Eruption and resorption anomalies
Many factors can influence the eruption of the tooth into the oral cavity. Osteoclasts play an important role in the formation of the eruption pathway so any interruption of their activity can alter eruption and resorption. Abnormalities of the periodontal ligament can also affect the retention of the teeth in the oral cavity and can, therefore, lead to early tooth loss or retention of primary teeth.
Eruption
The most important structure that controls eruption is the dental follicle. However, there needs to be an interaction between the dental follicle, the bone surrounding it and the tooth itself. This communication creates the proper pathway for eruption and any miscommunication or obstacles in the way (tooth, cyst, etc.) can alter the eruption mecanism.


Resorption
Resorption is a loss of dental structure and can be either internal or external. Internal resorption begins in the pulp and moves outwards whereas external resorption begins on the outer surface of the tooth. External resorption can be diagnosed on an X-ray. Many factors can influence resorption like orthodontic treatment, trauma, cysts, tumors, adjacent impacted teeth, infections, hormonal diseases, etc.
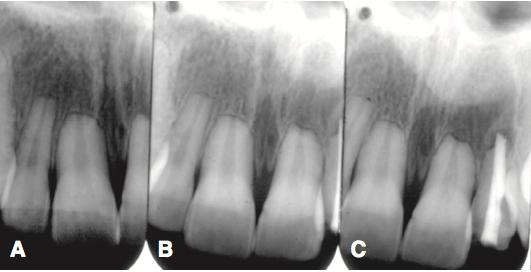

- Adel Kauzman, Faculté de médecine dentaire, Université de Montréal
- Rallan M, Rallan NS, Goswami M, Rawat K. Surgical management of multiple supernumerary teeth and an impacted maxillary permanent central incisor. BMJ Case Rep. 2013 May 22;2013.
- Kumar DK, Gopal KS. An epidemiological study on supernumerary teeth: a survey on 5,000 people. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013 Jul;7(7):1504-7.
- Cruz CV, Soares AL, Braga DN, Costa MC. Diagnosis and Surgical Management of Nonsyndromic Nine Supernumerary Teeth and Leong's Tubercle. Case Rep Dent. 2016;2016:8641867.
- White S, Pharoah M. (2014). Oral Radiology Principles and Interpretation. Missouri: Elsevier Inc.
